Radio-frequency identification (RFID) has undergone a resurgence as of late, with new technology that allows for its integration into nearly any type of tag or label. Manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs) represents one area that stands to gain enormously from RFID integration, mainly due to the limitations of barcode labels.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) has undergone a resurgence as of late, with new technology that allows for its integration into nearly any type of tag or label. Manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs) represents one area that stands to gain enormously from RFID integration, mainly due to the limitations of barcode labels.
Making the most of limited space
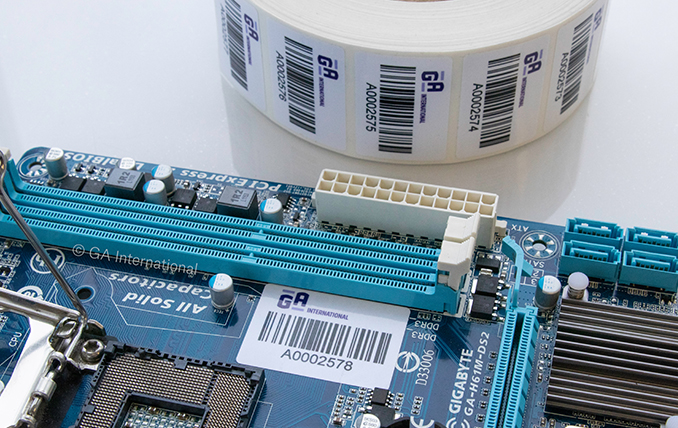
PCBs are notoriously difficult to identify. They are often relatively small, and with each new model, more and more space is devoted to functional use, leaving very little room for a tag or label. In this way, barcodes are severely limited due to the space they require. Though they are inexpensive, their information density is much lower compared with RFID.
Line-of-sight is another drawback to barcode label integration in PCBs. Because of this requirement, there are only so many areas on the PCB where the label can be placed so that the scanner can accurately and consistently read it. To make things even more complicated, label placement can affect the position of large heat sinks or mounting brackets, and once the PCB is in its final enclosure, the label will not be readable thereafter.
RFID tags solve these issues as they are available in smaller formats than barcode labels with more encodable information. Furthermore, because RFID scanning doesn’t require a direct line-of-sight, circuit boards can be identified regardless of their stage of development, and no new barcode label needs to be affixed if the old one becomes covered.
Labeling PCBs during manufacturing
A unique identifier is usually added to the board prior to the assembly process to enable automatic identification and traceability. However, during the PCB assembly process, components are applied on top of the board and soldered in place. This means labels must cope with high temperatures during the soldering process, in addition to the harsh chemicals used during the cleaning process. After soldering, the boards are washed at elevated temperatures to clean away any remaining solder flux and to prepare the board for further coating and bonding. The cleaning process can vary greatly and uses a combination of water, harsh solvents, pressurized sprays, and ultrasound to remove the unwanted residues.
As such, highly resistant labels are typically used to identify PCBs prior to assembly. Polyimide is typically the material of choice. If using RFID for improved tracking and traceability, it would be ideal to insert the inlay into a polyimide label. If labeling after the soldering process, less resistant labels can be utilized; tamper-evident labels are popular as they ensure that the serial number cannot be transferred to another board.
Better trackability and traceability
Circuit board manufacturing is a complex process, as components come packaged in what’s called a “tape and reel” format. Here, “reels” of components are loaded into tape feeders, which present the individual components to the machine as they are needed during assembly. PCBs require upwards of 100 to 200 of these components, including resistors, capacitors, switches, and LEDs. Some companies may manufacture nearly 5000 different types of boards in a single day. This means that to track and trace PCBs accurately, a system must be designed that minimizes errors and provides a means to distinguish errors throughout the assembly line.
RFID represents an upgrade over barcodes for all these requirements. Because of the enormity of information that can be stored, a single RFID tag can be used to identify specifics of the circuit boards throughout each step of assembly, ensuring that any recalls can be dealt with swiftly and accurately. RFID tags can also be used to determine the proper placement of components coming off each tape feeder. Finally, when the chips are assembled and shipped to stores, there is no need to re-label them with another barcode; the same RFID tags can be used throughout the entire distribution process and easily re-encoded when necessary.
Added security
Besides the ability to encrypt information with RFID, something that barcodes are incapable of doing, they can also be integrated with circuits themselves to provide additional security benefits. One application that’s been used is called a “lock in transit” system, where the CPU is locked immediately after manufacturing is complete. Once the board arrives at the store, it can be unlocked via a security code relayed through the RFID chip attached to it. Here, its primary use is to deter theft, as anyone who stole one of these chips would be unable to use or resell it.
Intel recently began using another security system called “Premise Aware Security” that utilizes RFID to limit access to specific information. An RFID tag could be allowed access to data regarding something confidential, like patient health charts, by transmitting information to a transponder on a motherboard, while it would be locked out in another area, like outside the department or the hospital itself.